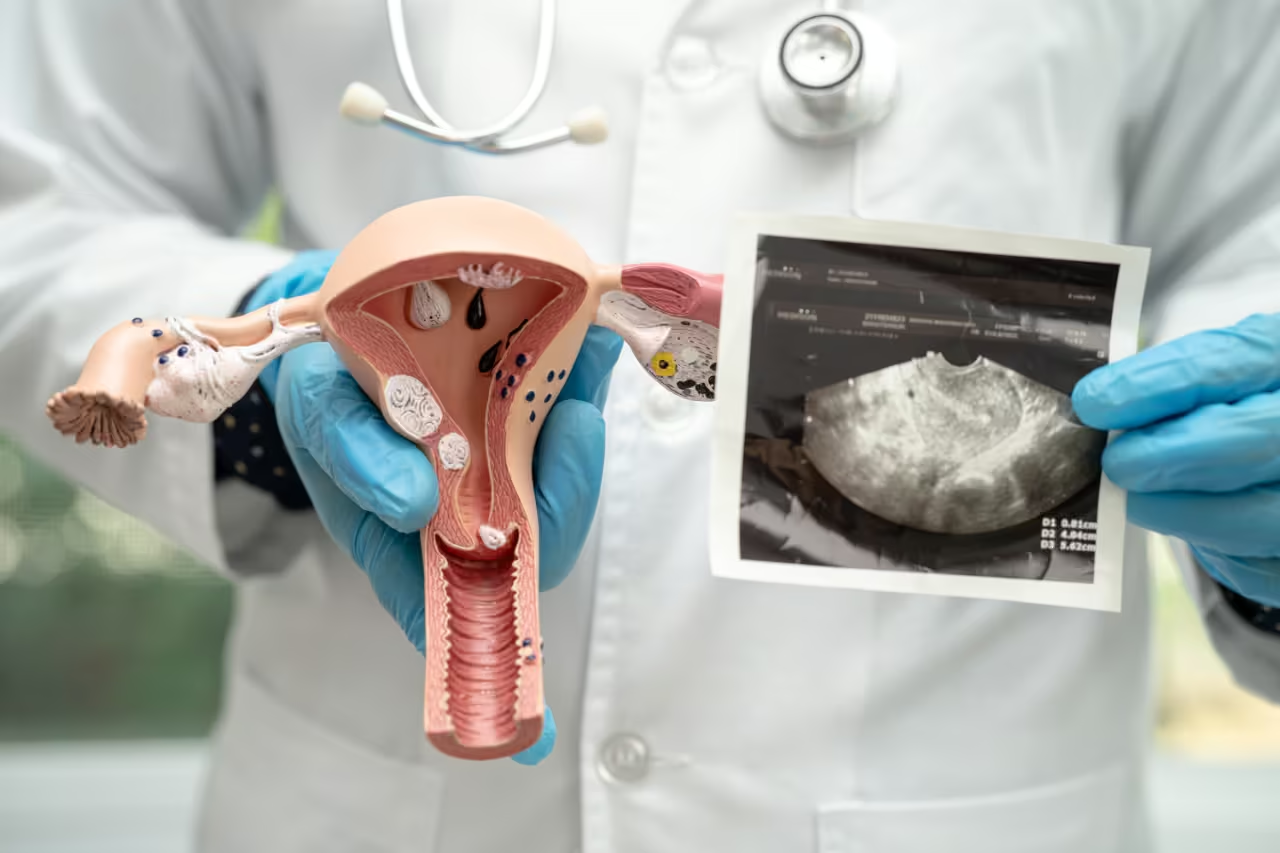
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets that develop in or on an ovary. These cysts are relatively common among women of childbearing age and, in many cases, are harmless and may go unnoticed. However, ovarian cysts can sometimes cause discomfort or pain and may lead to complications that require medical intervention. Understanding ovarian cysts, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options, is essential for individuals to manage this condition effectively and maintain reproductive health.
While most ovarian cysts are benign and self-resolving, some can persist and lead to more serious health issues. Knowing the different types of cysts and their potential impact can help individuals seek timely medical advice and treatment. Moreover, awareness and education about ovarian cysts can also play a crucial role in alleviating anxiety and empowering individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can vary significantly in size and type. Most ovarian cysts are functional, meaning they form as part of the menstrual cycle and are generally harmless. Functional cysts are typically related to the ovulation process, where an egg is released from the ovary. However, some cysts can be pathological, meaning they may not resolve on their own and could require medical attention or intervention due to potential complications.
Understanding the distinction between functional and pathological cysts is vital for effective management. While functional cysts are often transient and resolve without treatment, pathological cysts may present a range of symptoms and require closer monitoring. By recognizing the different types of ovarian cysts, individuals can better assess their symptoms and seek appropriate care when necessary.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
- Functional Cysts: These are the most common type of ovarian cysts and include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts. Follicular cysts occur when a follicle does not release an egg during the menstrual cycle, while corpus luteum cysts form after the follicle releases the egg. Both types typically resolve on their own without treatment, often disappearing within a few menstrual cycles. Despite their commonality, functional cysts can occasionally cause mild discomfort or irregular periods.
- Pathological Cysts: These cysts can be benign or malignant and include dermoid cysts, cystadenomas, and endometriomas. Dermoid cysts can contain various tissues, such as hair or skin, while cystadenomas can grow quite large and cause discomfort. Endometriomas, also known as “chocolate cysts,” are associated with endometriosis and can affect fertility. Pathological cysts often require medical evaluation to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include surgical intervention if they pose a risk to health.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and go unnoticed. However, when symptoms occur, they can include:
- Pelvic pain, often on one side, which may be sharp or dull and can vary in intensity. This pain may be intermittent or persistent, depending on the cyst’s size and location.
- Bloating or swelling in the abdomen, which can cause discomfort and a sense of fullness. This symptom can sometimes be mistaken for digestive issues or weight gain.
- Pain during intercourse, which can be due to pressure exerted by the cyst on surrounding tissues. This discomfort may affect sexual health and intimacy.
- Painful periods, characterized by increased cramping or heavy bleeding, which can disrupt daily activities and quality of life.
- Unusual bleeding, such as spotting between periods, which can be alarming and warrant medical evaluation to rule out other conditions.
If you experience sudden, severe pain, fever, or vomiting, seek medical attention immediately, as these could be signs of a ruptured cyst or other complications. Prompt medical evaluation is crucial in such cases to prevent further health issues and ensure appropriate treatment.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can develop for several reasons. Some common causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Irregularities in hormones, such as elevated estrogen or progesterone levels, can lead to the formation of functional cysts. Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can also contribute to cyst development.
- Pregnancy: Cysts can develop early in pregnancy to support the pregnancy until the placenta forms. These cysts, known as corpus luteum cysts, usually resolve on their own as the pregnancy progresses.
- Endometriosis: This condition, characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, can cause endometriomas to form on the ovaries. Endometriomas may lead to chronic pain and fertility issues.
- Pelvic Infections: Severe infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, can spread to the ovaries and cause cysts. Prompt treatment of infections is essential to prevent complications and preserve reproductive health.
Understanding these causes can help individuals identify potential risk factors and take preventive measures where possible. Regular check-ups and communication with a healthcare provider can also aid in early detection and management of ovarian cysts.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
To diagnose ovarian cysts, doctors often perform a pelvic exam. This examination allows healthcare providers to feel for any abnormalities in the ovaries or surrounding areas. If a cyst is suspected, additional tests may include:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test helps determine the cyst’s size, shape, and location. Ultrasound is a non-invasive and effective tool for visualizing ovarian cysts and assessing their characteristics.
- Blood Tests: These can help rule out other conditions and assess hormonal levels. Blood tests may also include checking tumor markers if there is a suspicion of malignancy.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure used to view the ovaries directly and potentially remove the cyst. Laparoscopy involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera to examine the pelvic organs, providing a clearer diagnosis and treatment option.
These diagnostic tools are essential for accurately identifying ovarian cysts and determining the best course of treatment. Early diagnosis can help prevent complications and ensure timely intervention when needed.
Treatment and Management of Ovarian Cysts
The treatment for ovarian cysts depends on the type, size, and symptoms. Options include:
Watchful Waiting
Many cysts, especially functional ones, resolve on their own. Doctors may recommend regular monitoring through follow-up ultrasounds to ensure the cyst doesn’t grow or cause complications. This approach is often suitable for asymptomatic cysts or those that are small and not causing any issues.
Medications
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Birth control pills can help regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new cysts. By stabilizing hormone levels, contraceptives can reduce the likelihood of functional cysts recurring.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage discomfort associated with cysts. These medications can provide relief from mild to moderate pain.
Surgical Options
- Cystectomy: Removal of the cyst while preserving the ovary. This procedure is often recommended for larger cysts or those that do not resolve on their own.
- Oophorectomy: Removal of one or both ovaries if the cysts are large or potentially cancerous. This option may be considered in cases where there is a significant risk to the patient’s health or fertility.
The choice of treatment depends on individual circumstances, including the patient’s age, symptoms, and reproductive goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate approach.
Natural Remedies for Ovarian Cysts
While medical treatment is often necessary, some individuals seek natural remedies to complement their care:
- Heat Therapy: A warm bath or heating pad can alleviate pain and provide comfort. Heat can help relax muscles and reduce cramping associated with ovarian cysts.
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbs like black cohosh and chasteberry may help regulate hormones and potentially reduce the occurrence of cysts. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Dietary Changes: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may support overall reproductive health. Reducing the intake of processed foods and increasing fiber can also help maintain hormonal balance and reduce inflammation.
These natural remedies can be part of a holistic approach to managing ovarian cysts. However, they should not replace medical treatment, especially in cases where intervention is necessary.
Complications of Ovarian Cysts
Though many ovarian cysts are harmless, potential complications include:
- Ovarian Torsion: A large cyst can cause the ovary to move, potentially twisting and causing severe pain. Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to prevent damage to the ovary.
- Rupture: A cyst can burst, leading to internal bleeding and intense pain. Ruptured cysts may require surgical intervention to prevent further complications.
- Infertility: Some types of cysts, particularly those associated with endometriosis, can affect fertility. Addressing these cysts through appropriate treatment can help preserve reproductive potential.
Awareness of these complications is crucial for timely intervention and preventing long-term health issues. Regular monitoring and communication with a healthcare provider can help manage these risks effectively.
When to Seek Medical Help
While ovarian cysts are often benign, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain: This could indicate a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion, both of which require urgent medical attention.
- Pain accompanied by fever or vomiting: These symptoms may suggest infection or other complications that need prompt evaluation and treatment.
- Symptoms that interfere with daily life: Persistent pain, bloating, or irregular periods that disrupt daily activities should be assessed by a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.
Seeking medical advice at the onset of concerning symptoms can prevent complications and ensure appropriate management of ovarian cysts.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological issue that many women will experience at some point. While often harmless, understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for effective management. Regular check-ups and communication with a healthcare provider can help monitor and address any concerns related to ovarian cysts.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can better navigate their reproductive health and seek appropriate care when necessary. Knowledge about ovarian cysts empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and fosters a proactive approach to managing potential issues.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can vary in type, with the most common being: Functional Cysts: These cysts form during the menstrual cycle and are usually harmless and short-lived. They are the most common type and are divided into two categories:
Follicular Cysts: These occur when the follicle fails to rupture and release its egg, continuing to grow into a cyst.
Corpus Luteum Cysts: After an egg is released, the empty follicle sac typically shrinks into a mass of cells called the corpus luteum. Sometimes, the sac doesn’t dissolve and instead seals off, filling with fluid.
Dermoid Cysts (Teratomas): These are more unusual cysts that can contain tissue, such as hair, skin, or teeth, because they form from embryonic cells.
Cystadenomas: These cysts form on the surface of an ovary and might be filled with a watery or a mucous material.
Endometriomas: These cysts grow as a result of a condition known as endometriosis, where uterine endometrial cells grow outside the uterus, including on the ovaries, and can form a cyst.Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are small and do not cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include: Pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst
Fullness or heaviness in the abdomen
Bloating
Painful bowel movements
Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
Pain during intercourse
Nausea, vomiting, or breast tenderness similar to that experienced during pregnancy
Large cysts can cause the ovary to move from its usual position, increasing the chance of painful twisting of the ovary, known as ovarian torsion. This can also decrease or stop blood flow to the ovary.Understanding Ovarian Cysts
At Newsense Clinic, our experts conduct thorough evaluations using ultrasound imaging to determine the size, type, and potential impact of the cysts. Understanding the nature of the cyst helps in deciding the most appropriate treatment approach. We offer a range of treatments for ovarian cysts, depending on their type and severity. Treatment options include hormonal therapies to regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the development of new cysts, as well as surgical interventions such as laparoscopy for cyst removal. Our ovarian cyst doctors in Dubai are skilled in both conservative and surgical treatments, ensuring that you receive the most suitable care for your specific condition.
Why Choose Newsense Clinic for Ovarian Cyst Treatment?
Choosing the right clinic for your ovarian cyst treatment is crucial. At Newsense Clinic, we pride ourselves on our: Expert Team: Our specialists are renowned for their expertise in gynecology and minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Advanced Technology: We use the latest diagnostic and treatment technologies to ensure optimal outcomes.
Personalized Care: Every treatment plan is customized to meet the individual needs and health goals of our patients.
Supportive Environment: We provide a supportive, understanding, and confidential environment, prioritizing your comfort and privacy.
Don’t let ovarian cysts affect your health and lifestyle. Contact Newsense Clinic today to schedule an appointment with our leading ovarian cyst doctors in Dubai. Your health is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.How can I prevent ovarian cysts?
While it’s not always possible to prevent ovarian cysts, regular pelvic exams and understanding the symptoms can help early detection and management. Hormonal contraceptives may help prevent the formation of new cysts in those who are prone to them.
What happens if an ovarian cyst ruptures?
A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause severe pain and internal bleeding. The severity of the symptoms depends on the size of the cyst, the extent of the rupture, and whether the cyst was causing infection or involving blood vessels.
Can ovarian cysts prevent pregnancy?
Most ovarian cysts do not affect fertility. However, certain conditions like endometriosis-associated cysts (endometriomas) can impact fertility. Functional cysts typically do not interfere with pregnancy.
Are ovarian cysts cancerous?
Most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and harmless, especially those that occur during the reproductive years. However, a small number of cysts could be malignant (cancerous), especially in postmenopausal women.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage ovarian cysts?
Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and a balanced diet can help, although these changes do not directly prevent cysts. They can, however, improve your overall health and hormonal balance.